LSI first, range chemistry second

What if range chemistry is the wrong thing to focus on when managing water? What if the ranges do not always apply, like in the winter? Theoretically, the textbook ranges for chemistry are ideal. But in reality, that's not always the case. In this article we will explain why we prioritize the Langelier Saturation Index (LSI) first, and range chemistry after that.
Covered in this article:
- What is the LSI?
- What is "range chemistry"?
- What's wrong with range chemistry?
- LSI balance is what water wants
- What LSI-focused chemistry targets look like
- simplify. simplify. simplify.
- Conclusion
What is the LSI?
The Langelier Saturation Index (LSI) is a formula for measuring how balanced water is, based on the saturation equilibrium of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). We elaborate on LSI in many other articles if you would like to take a few minutes to dive deeper:
- LSI Balance and Calcium Management | Pillar 1
- Understanding the Langelier Saturation Index (LSI)
- Cold water and the LSI
- What is the LSI? | Orenda Help Center
The importance of the LSI cannot be understated. Water will never read pool industry textbooks and it does not care about individual chemistry factors. It cares about equilibrium of calcium carbonate saturation. The LSI is the internationally-best-known index for measuring this equilibrium. So pay attention to it! LSI balance is what water wants.
The LSI Factors
The LSI has six factors. If borate is used in your water, it is a seventh factor.
- pH
- Carbonate alkalinity
- Calcium hardness
- Water temperature
- Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), including salt
- Cyanuric acid (CYA)
- [Borate] only if used
Do you test for ALL these factors on your pools? If so, how often? Each of them impact water balance. We recommend testing pH, total alkalinity and water temperature each and every week. The other factors–calcium hardness, CYA, and TDS–should be tested monthly, because they do not change rapidly.
The habit of many pool professionals is to test chlorine, pH and sometimes alkalinity. But that's only one-third of the LSI factors (at best). What is not measured cannot be managed.
What is "range chemistry"?
When you read textbooks, manufacturer guidelines and anything else that gives ranges for individual chemistry factors, that's what we consider range chemistry. For instance, here's a table recreated from various textbooks and sources in the industry. These are not our opinion, they are just conventional wisdom from the swimming pool industry.
| Factor | Minimum | Maximum | Ideal |
| pH | 7.2 | 7.8 | 7.4-7.6 |
| Total Alkalinity (TA) | 60 ppm | 140 ppm | 80-120 ppm |
| Calcium Hardness (CH) | 200 ppm | 400 ppm | 200-400 ppm |
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) | n/a | 1500 ppm over tap | < 1500 ppm over tap |
| Cyanuric Acid (CYA) | 0 | 100 ppm | 30-50 ppm |
| Combined Chlorine | n/a | 0.5 ppm | <0.2 ppm |
These are ranges. So when we say "range chemistry", we're referring to this mindset of focusing on each individual factor conforming to a prescribed range.
What's wrong with range chemistry?
It's not that all the ranges themselves are wrong...it's that they often trap pool owners and operators into impossible situations. In other words, it is entirely possible–and common–that pools within textbook ranges still violate the LSI. And again, LSI balance is what water cares about. Water doesn't care that you're doing your best to follow instructions; it is either balanced or is is not. And if not, water must balance itself.
For instance, use the Orenda Calculator and adjust the water chemistry into the middle of the ideal ranges. At normal swimming temperatures (say, about 82ºF or 28ºC). You should be LSI balanced at those levels, and that's great! But will you stay balanced? Can you maintain a pH between 7.4 and 7.6 for a week? Have you ever been able to, without a chemical controller, trichlor feeder or automatic pool cover?
No? Because neither have we. Nobody can, because it's physically impossible with 80-120 ppm total alkalinity. This is because of Henry's Law of physics.1
The physical reality of pH rising is just one of many conflicts between individual ranges and LSI balance. Cold water can make otherwise "perfect water" violate the LSI and become aggressive. Where is the range for water temperature? Are we expected to control water temperature year-round with heaters? Of course not. But water temperature matters!
LSI balance is what water wants
Ranges can be beneficial if used properly. We want to challenge the mindset of many pool professionals, which presumes all will be fine as long as the ranges are in line. For many pools, that's simply not true during most of the year.
Not only will pH naturally rise above 7.8 when you have 80-120 ppm total alkalinity, but having a shortage of calcium hardness risks permanent damage to the pool and its equipment. Indeed, maintaining LSI balance year-round2 is impossible without violating some ranges along the way (particularly during the winter).
So our message is simple: LSI first, range chemistry second. If you're going to use ranges to guide you, make sure they fit within the context of the LSI. If you're violating the LSI, water will have to correct itself. And while we have thousands of ways to balance water, water only has two ways to balance itself: eat or scale.
If you find yourself unable to maintain LSI balance within the textbook ranges, you are not alone. Particularly when the water is cold, you need to break a few eggs to make this omelet. It's okay to have more than 400 ppm calcium hardness in the winter. In fact, we strongly encourage doing so if you know your pool is going to freeze. And when closing a pool for the winter, it's okay to let the pH naturally rise to its ceiling IF the LSI is balanced when the pH gets there.
What LSI-focused chemistry targets look like
When we change our mindset from chasing pH and instead focus on balancing the LSI, the value of calcium becomes undeniable. Calcium hardness is the foundation we build our water chemistry strategy upon. The lower the calcium, the fewer options to balance the LSI.
Most swimming pools will need a calcium hardness level between 250-500 ppm, depending on the water temperature. The primary sanitizer type dictates the recommended total alkalinity. Trichlor is acidic, and therefore, more TA is needed. But liquid chlorine and cal hypo are basic, so less TA is needed. Saltwater pools need even less than that to prevent issues like calcium flakes. But by and large, most swimming pools will use between 60-90 ppm TA.
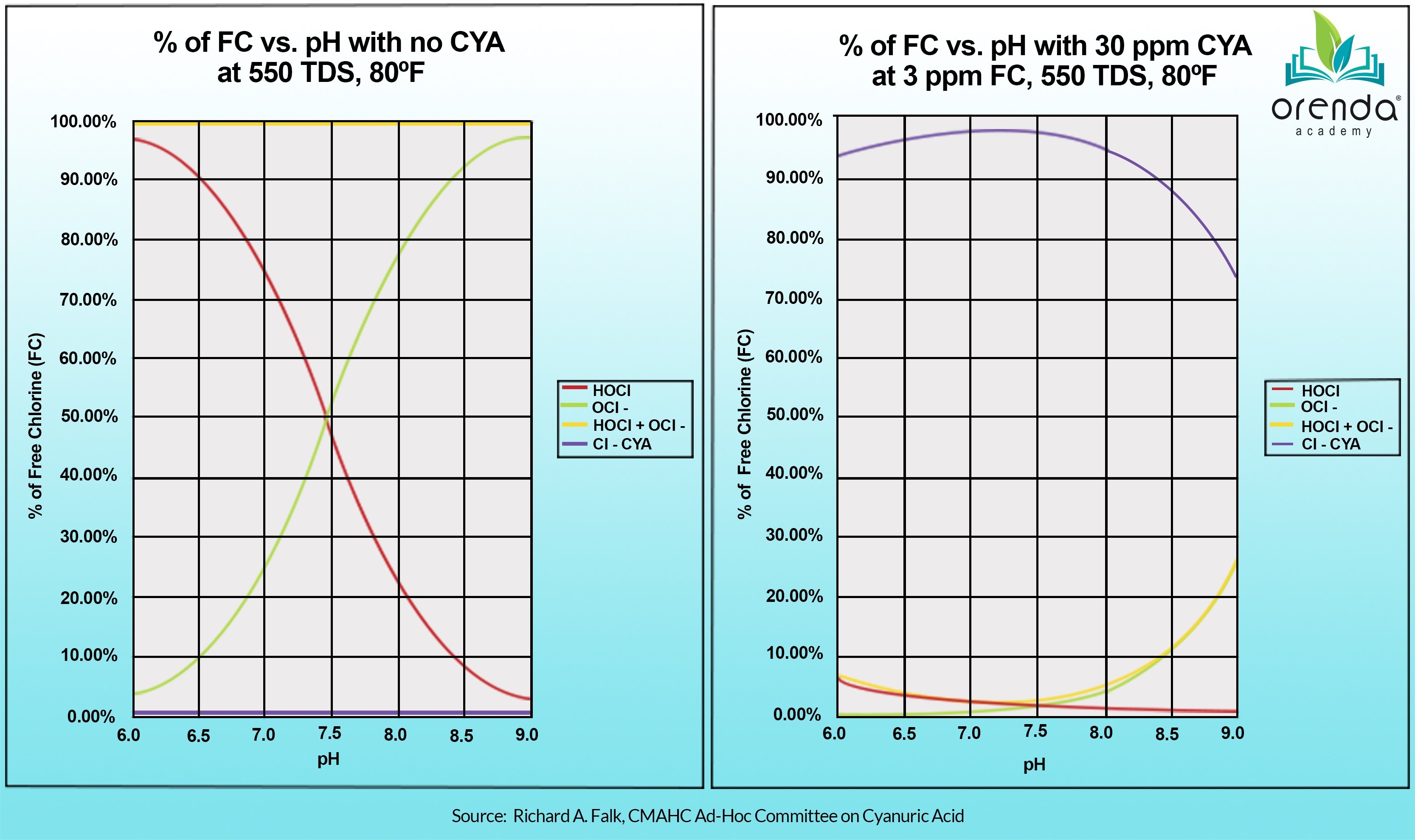
Cyanuric acid (CYA) should be kept below 50 ppm in all outdoor pools, if possible.
Finally, the pH. Yes, we mention it last on purpose because we do not aim to control pH. We aim to contain pH. There is a difference. We instead focus on making sure the pH ceiling is low enough so that when the pH naturally rises to it, the LSI remains balanced. In that context, we allow the pH to naturally rise to its ceiling in outdoor pools that have CYA in them. For non-stabilized pools, pH is far more important because of its impact on chlorine speed (%HOCl).
simplify. simplify. simplify.
An Orenda pool is one that uses the least amount of chemicals possible. It has a robust foundation of calcium hardness, an appropriate total alkalinity based on the primary sanitizer type, which in turn dictates a pH ceiling that allows for LSI-balance year-round. An Orenda pool is never over-stabilized with CYA over 50 ppm, and water temperature is always taken into account every time the pool is tested and treated.
Conclusion
LSI first, range chemistry second. This is because water cares about equilibrium (LSI), not individual chemistry parameters. It's okay to look at individual factors as long as they are viewed within the context of the overall LSI of the water. This is important because textbook "balanced water" is often unbalanced on the LSI. This is especially true in the winter.
For more information on how to balance your pool according to the LSI, you can listen to our podcast or continue to search our site...we talk about how to do this extensively in other articles.
1 This topic is a deep rabbit hole that we have written and spoken extensively about on our blog, help center, and podcast (episodes 1,2,3,29,35,46,69,91 and 101). Here's a quick overview: pH will naturally rise if you have carbonate alkalinity in your water (which every swimming pool should). So while it matters where your pH is today, it also matters where it's going to be when you get back. We have a secondary reading in the Orenda Calculator™ called "pH ceiling" that shows you exactly where the pH is trying to rise to. This is only possible to calculate thanks to carbon dioxide and Henry's Law of the solubility of gases. So instead of trying to control pH (which is impossible), work to contain pH. Range chemistry does not account for this law of physics, and therefore leaves weekly pool care in an impossible position, where everyone is practically guaranteed to violate at least the pH range each week.
2 Maintaining LSI balance year-round is the action step for our First Pillar of Proactive Pool Care.
